Know how deadly ‘Blast over Pressure’ is?
Overpressure (or blast overpressure) is the
pressure caused by a shock wave over and above normal atmospheric pressure. The shock wave may
be caused by explosion
or sonic boom.
A measured over pressure is basis to know the effects of nuclear explosion or
bomb explosion. The injury caused by the blast over pressure is known as blast
injury.
Mechanism
Blast injuries can result from various types of incidents ranging from industrial accidents to terrorist attacks. High-order explosives produce a supersonic overpressure shock wave, while low order explosives deflagrate and do not produce an overpressure wave. A blast wave generated by an explosion starts with a single pulse of increased air pressure, lasting a few milliseconds. The negative pressure (suction) of the blast wave follows immediately after the positive wave. The duration of the blast wave depends on the type of explosive material and the distance from the point of detonation. The blast wave progresses from the source of explosion as a sphere of compressed and rapidly expanding gases, which displaces an equal volume of air at a very high velocity. The velocity of the blast wave in air may be extremely high, depending on the type and amount of the explosive used. An individual in the path of an explosion will be subjected not only to excess barometric pressure, but to pressure from the high-velocity wind travelling directly behind the shock front of the blast wave.
The magnitude of damage due to the blast wave is dependent on the
a) Peak of the initial positive pressure wave,
b) the duration of the overpressure,
c) the medium in which it explodes,
d) the distance from the incident blast wave,
and
e) the degree of focusing due to a confined
area or walls.
For example, explosions near or within hard
solid surfaces become amplified two to nine times due to shock wave reflection.
As a result, individuals between the blast and a building generally suffer two
to three times the degree of injury compared to those in open spaces.
Effects
of overpressure
"Blast overpressure (BOP), also known as
high energy impulse noise, is a damaging outcome of explosive detonations and
firing of weapons. Exposure to BOP shock waves alone results in injury
predominantly to the hollow organ systems such as auditory, respiratory, and
gastrointestinal systems.
|
|
||||||||
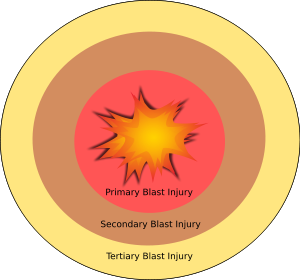
Classification
The effects of Blast injuries are divided into
four classes: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
Primary injuries
Primary injuries are caused by blast overpressure
waves, or shock waves.
These are especially likely when a person is close to exploding ammunition,
such as a land mine. The ears are most often affected by the overpressure,
followed by the lungs and the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal
injuries may present after a delay of hours or even days. Injury from blast
overpressure is a pressure and time dependent function. By increasing the
pressure or its duration, the severity of injury will also increase.
Blast lung refers to severe pulmonary contusion, bleeding or swelling with damage to
alveoli and blood vessels, or a combination of these. It is the most common
cause of death among people who initially survive an explosion.
Secondary injuries
Secondary injuries are caused by fragmentation and other objects propelled
by the explosion. At times the propelled
object may become embedded in the body, obstructing the loss of
blood to the outside. However, there may be extensive blood loss within the body cavities.
Fragmentation wounds may be lethal and therefore many anti-personnel bombs are designed to
generate fragments.
Most casualties are caused by secondary
injuries as generally a larger geographic area is affected by this form of
injury than the primary blast site as debris can easily be propelled for
hundreds to thousands of meters. In other instances, the target provides the
raw material for the objects thrown into people, e.g., shattered glass from a
blasted-out window or the glass facade of a building.
Tertiary injuries
Displacement of air by the explosion creates a
blast wind that can throw victims against solid objects. Injuries resulting
from this type of traumatic impact are referred to as tertiary blast injuries.
Tertiary injuries may present as some combination of blunt and penetrating
trauma, including bone fractures and coup contre-coup injuries. Children are at
a particularly higher risk of tertiary injury due to their relatively smaller
body weight.
Quaternary injuries
Quaternary injuries, or other miscellaneous
named injuries, are all other injuries not included in the first three classes.
These include flash burns, crush
injuries, and respiratory injuries.
Protection
against Blast over pressure
- The design and layout of the process area should be such as to avoid generation of vapour/dust of the materials that can form explosive mixture with air
- The handling area must be provided with flame proof/spark proof fitting of electrical appliances.
- The confined area must be provided with excessive pressure relief mechanism to avoid build up of over pressure
- The process should be monitored with latest designed instrumentation and CCTV to keep vigilance on unsafe practices.
- An EOD suit can protect against the deadly effects of BOP.
Courtesy: Wikipedia and Toxicological Sciences,
Shared
by www.safetitude.com
in general interest of all people concerned

Comments
Post a Comment